Dental implants have revolutionized the world of tooth replacement, offering a durable and natural-looking solution for missing teeth. Understanding what dental implants are and recognizing the importance of their longevity can make a significant difference in your oral health journey.
What Are Dental Implants?
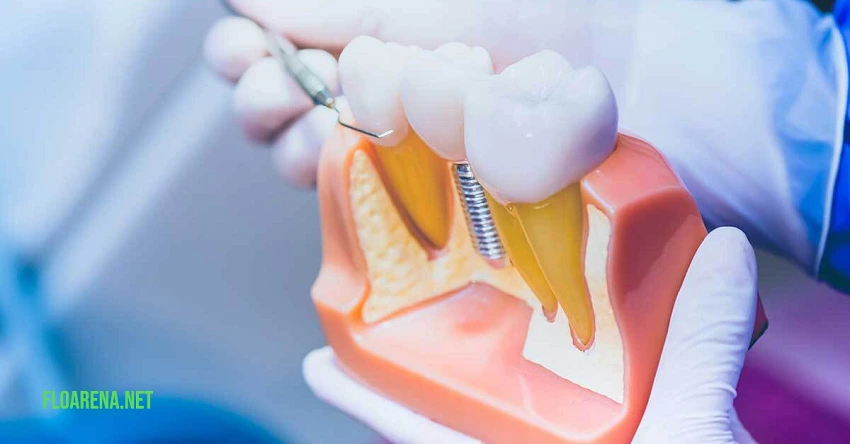
A dental implant is essentially a titanium implant that acts as an artificial root, providing a foundation for fixed or removable prosthetic teeth. These implants are designed to blend seamlessly with your natural teeth, both in terms of function and aesthetics. The process of osseointegration, where the implant fuses with the bone, ensures the stability and durability of the implant. With the right care and conditions, dental implants can offer numerous benefits, from improved speech and comfort to enhanced oral health.
Factors Affecting Dental Implant Longevity
Dental implants have emerged as a preferred solution for tooth replacement due to their durability and functionality. However, the longevity of a dental implant can be influenced by several factors:

Materials Used in Implants
The majority of dental implants are made of titanium because of its biocompatibility and resilience. The quality and grade of titanium can impact the implant’s durability.
Quality of Surgical Procedure
A meticulous surgical procedure by a skilled dental surgeon is vital. An improperly placed implant can lead to complications, affecting its lifespan.
Individual’s Oral Hygiene Habits
Regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings are essential. Poor oral hygiene can lead to infections around the implant.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Conditions like diabetes or osteoporosis can impact healing and the bone’s ability to fuse with the implant, potentially affecting its success.
Bone Quality
Adequate bone density is crucial for the implant’s stability. In cases of insufficient bone, procedures like bone grafting might be needed.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Both can impede the healing process post-surgery and have been linked to higher implant failure rates.
Post-Operative Care
Following the dentist’s post-operative care guidelines, such as avoiding certain foods and maintaining hygiene can prevent complications.
Oral Environment
The pH level of the mouth, often affected by diet and other factors, can influence the health of tissues around the implant.
Prosthetic Overload
If the prosthetic tooth (crown) attached to the implant isn’t aligned properly, it can cause undue stress on the implant, leading to complications.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular visits allow early detection of potential issues. The dentist can identify and address any signs of gum disease, implant loosening, or other concerns before they become major problems.
Practical Steps to Ensure Dental Implant Longevity
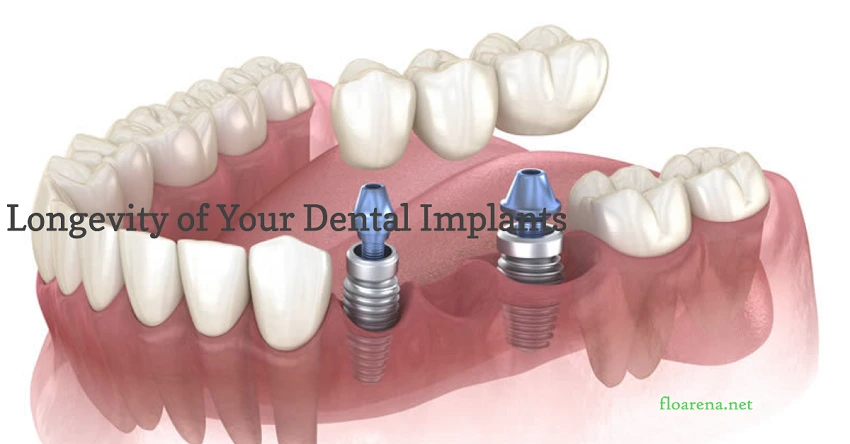
Ensuring the longevity of dental implants requires a combination of professional dental care and personal oral hygiene practices. Here are ten practical steps to help maximize the lifespan of your dental implants:
Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene
Brush your teeth twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Floss regularly, especially around the implant area, to remove any trapped food particles.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Schedule visits to your dentist every six months. These check-ups allow for early detection and treatment of potential issues.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking restricts blood flow to the gums, which can hinder the healing process and lead to implant complications.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol can weaken the bone structure and interfere with the osseointegration process of the implant.
Wear a Mouth guard
If you play contact sports or have a habit of grinding your teeth, wearing a mouth guard can protect your implant and surrounding teeth from potential damage.
Avoid Chewing Hard Foods
Biting down on hard items, like ice or hard candy, can damage the crown or even the implant itself.
Use an Antibacterial Mouthwash

This can help in preventing infections and keeping the gums healthy around the implant site.
Attend Follow-up Appointments
After the implant procedure, ensure you attend any scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor the implant’s progress.
Protect Against Gum Disease
Regular cleanings and an oral hygiene routine can prevent periodontal disease, which can lead to implant failure if left untreated.
Stay Educated
Stay informed about the latest care techniques for dental implants. Your dentist or oral surgeon can provide guidance and resources.
By following these practical steps, you can play a proactive role in ensuring the longevity of your dental implants, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of a healthy and complete smile for many years to come.
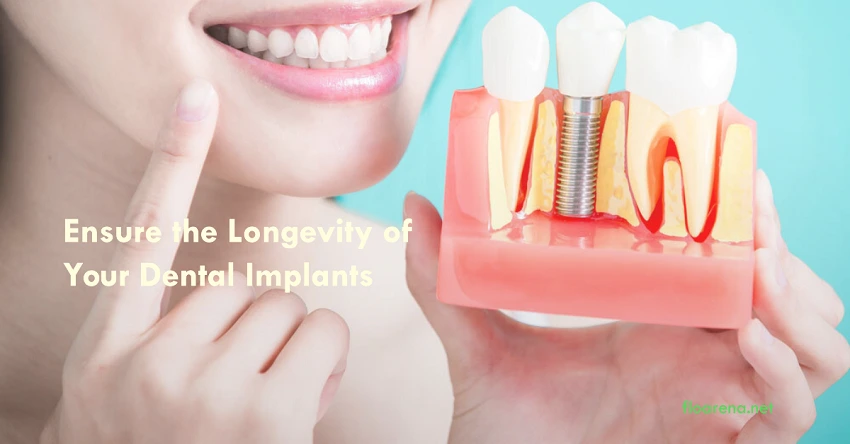
Signs Your Dental Implant Needs Attention
While dental implants have a high success rate, like any medical procedure, they’re not without potential complications. It’s crucial to recognize early signs that might indicate your implant needs professional attention:
Persistent Pain or Discomfort
While some pain is expected immediately after the implant procedure, if the pain persists or returns after a period of comfort, it could indicate a problem. This might be due to implant movement, infection, or damage to nearby nerves.
A Feeling that the Implant is Loose
Stability is a hallmark of a successful dental implant. If you start to feel movement in the implant, it might not have integrated properly with the bone, or there could be an issue with the abutment (the part connecting the implant and the crown).
Swelling, Redness, or Signs of Infection around the Implant Site
Minor swelling is typical post-surgery but should subside within a few days. Persistent or returning swelling, especially when accompanied by redness or warmth, might indicate an infection or peri-implantitis, a condition where the gum and bone around the implant become inflamed.
Difficulty or Pain while Chewing
A well-fitted implant should restore the natural function of a tooth. If you experience pain or difficulty while eating, it could suggest that the implant is not aligned correctly or that there’s an issue with the prosthetic.
Gum Recession around the Implant
If the gum tissue starts to recede and expose more of the implant or metal post, it might be due to gum disease or improper placement of the implant.
Bad Breath or an Unpleasant Taste
Persistent bad breath or a foul taste, especially when combined with other symptoms, could be a sign of infection or peri-implantitis.
Pus around the Dental Implant
The presence of pus is a clear sign of infection and requires immediate attention.